What is meant by Socket Bone Grafting?
Socket graft (or) Socket preservation graft is a form of dental bone grafting procedure. It is used to protect the empty socket after extracting a tooth. The socket is a bony crypt in the jaw surrounded by connective tissues to anchor a tooth. When a tooth is removed surgically, the bone around the empty socket gradually deteriorates, causing jaw bone loss.
Socket preservation is designed to protect and even rebuild the bone in such empty tooth sockets.
Table of Contents
Why should you get socket preservation after tooth extraction?
When a tooth is pulled out surgically or knocked out, the jawbone begins to change from the very next minute. Once our body detects the absence of a tooth, it starts to destroy the supporting tissues of the missing tooth to conserve energy and blood supply.
It pushes the bony ridge (also known as the alveolar ridge) that surrounds the tooth root to hold the socket begins to collapse and eventually disappears. This is followed by shrinking the remaining bone structures.
Socket preservation graft intends to slow down such shrinkage process (or bone deterioration) so that the jaw bone’s natural width and height in the extraction site are preserved. Thus your jaw bone volume is conserved and hence you can get implant teeth restorations later.
Mostly, dentists perform socket grafts immediately after extracting a tooth. It means you can get it done concurrently with a dental extraction in a single clinical visit. Meanwhile, socket grafting costs lesser than other dental bone graft techniques.
What is involved in the Socket preservation graft procedure?
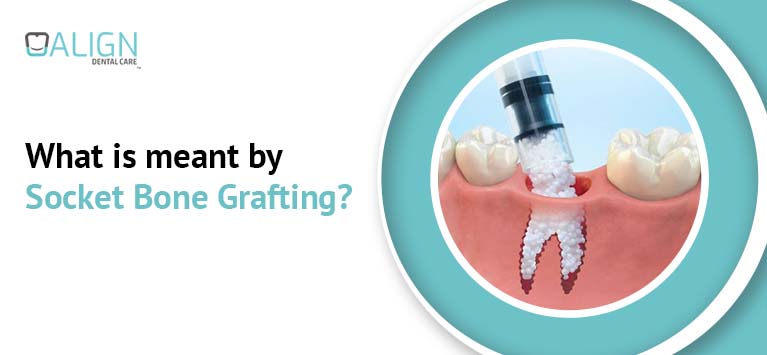
When a dentist removes a tooth surgically, the empty tooth socket is thoroughly cleaned to eliminate the remaining root particles. Now, graft material is placed directly inside the socket.
There are numerous bone grafts available and are made up of synthetic materials. Mineralized freeze-dried bone allograft is the widely used graft material for socket bone preservation procedures. In certain cases, other graft materials are preferred to suit the unique needs of a patient. Similarly, a bone taken from other parts of your body is also utilized for graft.
Dentists use radiographs to ensure that a sufficient amount of graft material is placed. The grafts provide a foundation for rebuilding the bone. Now, a foam-like membrane is placed over the graft and the gum segments are sutured.
The grafts integrate with the existing bone to generate a new bone in the extraction socket during the healing phase.
However, the socket grafts cannot last forever. Over time, it begins to collapse so dentists recommend to implant teeth within 4 to 6 months after socket grafting. If you prefer dental bridges to restore the missing tooth, get it done within 3 months after this ridge preservation procedure.
What are the advantages of getting a socket graft?
Besides counteracting the two dimensions of bone loss (Horizontal width & Vertical height) occurring after losing a tooth, the socket preservation procedure provides certain benefits as follows:
- Correct deformities in the alveolar ridge
- Preserves jaw health and structure
- Prevent teeth shifting
- Assures bone gaps between the remaining teeth stay firmly in their places
Bottom line
Socket preservation involves placing bone graft materials in the extraction socket. The treatment aims at preserving or rebuilding the alveolar ridge by impeding the naturally occurring bone shrinkage after losing a tooth. Hence it is also known as the ridge preservation procedure.
Even though it protects the jaw bone’s integrity and provides a foundation for implants, you can benefit from it only if you get the dental implants quickly after the socket graft procedure.