What everybody should know about oral mucocele?
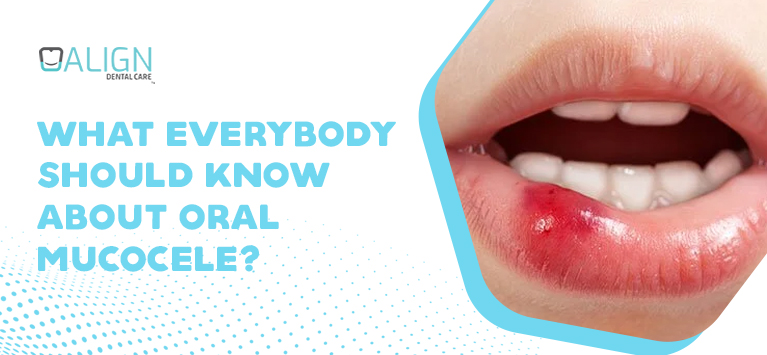
Do you notice any swollen spots inside your mouth? Is it appear translucent bluish color and bothersome while doing oral activities? If yes, it might be an oral mucous cyst.
Oral mucous cyst, also known as Mucocele is a harmless, fluid-containing cyst that appears in certain areas inside the oral cavity. It occurs due to various reasons and goes on its own in most cases. However, it necessitates in-office treatments at times.
What causes Oral Mucous Cysts?
Mucocele (Oral Mucous Cysts) happens due to various reasons and is highly seen in kids and young adults. Mostly, cysts appear on the lower lip and gums. In particular cases, the fluids collect in the palate or roof of the mouth. They are termed Ranula.
Saliva produced by salivary glands travels through a tiny tube called salivary gland ducts to reach our mouths. When the ducts are damaged to accidental bites or injuries, mucus (the slippery fluid produced by the linings inside the mouth) accumulates and forms a cyst-like swelling. In certain cases, the salivary gland ducts are blocked so that mucus gets congested that sums up the formation of cysts.
The possible factors that tend to damage the ducts are responsible for the fluid-filled lumps. The important things to mention are:
- Oral piercings
- Lip biting
- Particular ingredients in toothpaste (for some people)
Usually, the cysts are small and sized between 2 and 10 mm in diameter. However, they are large at times and cause more discomforts in speaking, chewing, swallowing.
How do dentists classify oral mucous cysts?
Mucoceles have been classified as follows:
- Extravasation mucocele – Caused by damage in the salivary gland ducts.
- Retention mucocele – It is commonly seen in aged persons and is caused due to blockage of salivary gland ducts.
Besides this, oral mucous cysts are classified based on the position they occur:
- Classic mucocele – Cysts develop on the upper layer of the submucosa
- Deep mucocele – Cysts develop on the lower layer of mucous membrane
- Superficial mucocele – Cysts develop under the mucosal surface.
How do dentists diagnose mucocele?
Besides the swollen spots, mucocele can be identified with 8ound or dome-shaped bluish-colored spots. Meanwhile, dentists decide if such atypical looking swollen spots are oral mucous cysts using
- CT Scan
- Dental X-rays
- Ultrasound
- Biopsy
What are the treatment options dentists have to fix mucocele?
As mentioned earlier, it is a harmless condition and can repair on its own in a few days. In certain cases, the cysts exist for a while. In such cases, don’t try to treat yourself because it may cause further damage thereby the affected spot will be easily affected.
If a dentist diagnoses a damaged salivary gland duct, then he/she will any of the following 2 procedures:
- Remove the salivary gland
- Helps to form a new salivary gland duct. This technique is called marsupialization.
Usually, dentists follow surgical procedures. Nowadays, advanced solutions like laser therapy and cryotherapy are also available to treat damaged ducts in salivary glands.
Bottom line
Mucocele is an acute, benign condition formed due to the congestion of fluids due to blockage in salivary glands or damage in salivary gland ducts. Despite it can be treated easily, the sufferer should keep the areas around the cyst clean to prevent infection.
When you feel the cysts are more troublesome, consult your dentist immediately. Home remedies like warm compress, tea tree oil would provide you temporary relief. If you want the right home remedies for oral mucous cysts, contact our dentists in dehiwala.