Dental cysts – Everything you need to know
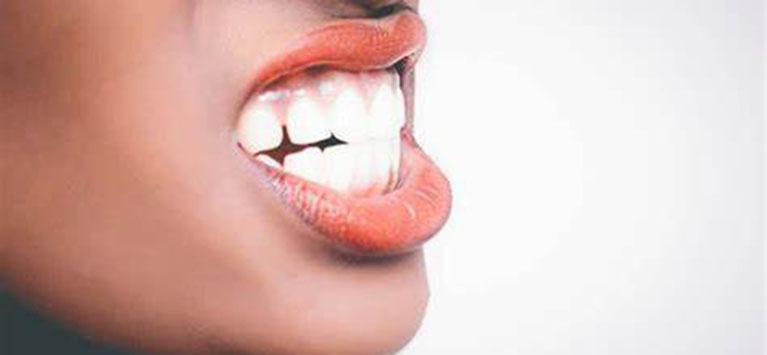
Dental cysts are defined as closed cavities filled with a fluid-like material. Such fluid-filled sacs are typically formed and develop gradually around the jaw bone, and gums near the crown of a partially erupted tooth, especially molars and canines.
Teeth are more delicate in their development stage than erupted teeth, making the unerupted teeth more susceptible to dental cysts.
Even though dental cysts are harmless in most cases, they will lead to serious complications if the closed-off cavities (cysts) remain untreated. It is asymptomatic in its initial stages but it exhibits a variety of symptoms when the cysts grow more than 2 centimeters in diameter.
Table of Contents
What are the symptoms of dental cysts?
Once the fluid-filled sac is formed and starts to grow, you will notice the following signs:
A small bump on a partially emerged tooth
• Tooth displacement
• Space between the displaced teeth
• Teeth Sensitivity
• Loose teeth
• Puffy gums
• Numbness in the face
The dental cysts are usually occurring in secondary teeth hence that the condition is highly seen in people who are in their 20s and 30s. However, it is quite uncommon in children.
What causes dental cysts?
The exact cause of this oral complication is unknown. Some people inherit it genetically. Likewise, various factors tend to pile up fluids over the crown portion of an impending tooth. The most possible causes include:
- Gorlin’s Syndrome – A rare genetic disorder that affects various organs. It is highly linked to developing odontogenic tumors that include dental cysts as a subtype.
• Poor craftsmanship in Root Canal Treatment. In such cases, the fluid-filled sacs will develop in the pulp chamber.
• Teeth that grow in an abnormal position
• Impacted wisdom teeth
The dental cysts are categorized based on the potential cause and the area in which the fluid-filled sacs are formed.
What are the different types of dental cysts?
Dental cysts are classified into 3 types as follows:
Periapical Cyst – The periapical cysts occurs when the pulp is inflamed due to injuries or deep cavities. In such cases, the infected pulp releases toxins that accumulate at the end of the root tip, causing cysts. This condition is also known as root end cyst, apical periodontal cyst, and radicular cyst.
• Dentigerous Cyst – It is formed over the crown portion of a tooth that is about to erupt. This kind of cyst is highly occurring in lower wisdom teeth and upper canine teeth. The fluid-filled sacs formed exert pressure over the erupting teeth and as a consequence, the blood flow is obstructed due to which the fluid gets deposited between the tooth’s coronal portion and enamel membrane.
• Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumors (KCOTs) – The root cause of this cyst type remains a myth. However, dentists believe that the cyst is formed at the pace of a tooth. On the other hand, the KCOTs can develop again even after treating them. Hence dentists tend to surgically remove the teeth that contain this kind of dental cyst.
Will the dental cysts go on their own?
The dental cysts do not heal themselves without any therapeutic intervention. Antibiotics can provide temporary relief alone. Hence dental support is necessary to completely get rid of dental cysts.
How do dentists treat dental cysts?
By simply looking at the odontogenic tumors, dental doctors can detect whether it is a dental cyst and its type. However, the cysts might be difficult to spot if they are small. Hence dental doctors utilize imaging systems like X-rays to identify the cysts and confirm it with CT Scan or MRI Scan.
Then, based on the cysts’ sizes, a treatment choice is determined. For small-sized cysts, dentists would remove the tumor along with the affected tooth. For large-sized cysts, a minor surgical procedure called “Marsupialization” is recommended.
Marsupialization involves making an incision in the cyst and folding the edges of the slit. The incision allows the cyst remains open and drain the fluid the cyst contains. In complex conditions, this technique has to be done more than once.
In certain cases, Root Canal Therapy, Reconstruction procedures are required to get rid of the dental cysts completely.
Bottom line
The dental cysts seem harmless in most cases. It does not mean you can leave it untreated. It is a kind of odontogenic tumor and shows symptoms only when they grow bigger. Hence it is better to consult your dentist if you notice your teeth become loose and start to displace suddenly for no reason.
Removing the dental cysts promptly will help you to avoid various complications like tooth loss, jaw fracture, etc.