How to Get Instant Relief from Burning Mouth Syndrome?

Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a perplexing condition characterized by a persistent burning sensation in the mouth, often affecting the tongue, lips, gums, palate, or throat. This discomfort can significantly impact daily activities such as eating, speaking, and sleeping. In this blog, we will explore what BMS is, its symptoms, potential causes, treatments, home remedies, and preventive measures to help you find relief and manage this condition effectively.
What Is Burning Mouth Syndrome?
Burning Mouth Syndrome is a chronic condition that causes a burning or scalding sensation in the mouth without an apparent cause. This sensation can be continuous or intermittent and may persist for months or even years. BMS is classified into two types:
- Primary BMS: Occurs without an identifiable medical condition and is often linked to nerve dysfunction.
- Secondary BMS: Results from an underlying medical condition such as nutritional deficiencies, oral infections, or certain medications.
Burning Mouth Syndrome Symptoms
Individuals with BMS may experience:
- Burning Sensation: A feeling of scalding or burning in the mouth, particularly on the tongue, lips, gums, palate, or throat.
- Dry Mouth: A sensation of dryness despite normal saliva production.
- Altered Taste: Changes in taste perception, such as a metallic or bitter taste.
- Tingling or Numbness: Unusual sensations like tingling or numbness in the mouth.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may be absent during sleep but worsen as the day progresses.
What Causes Burning Mouth Syndrome?
The exact cause of BMS is often difficult to determine, especially in primary BMS. However, several factors have been associated with secondary BMS, including:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and B vitamins can contribute to BMS.
- Oral Conditions: Issues such as dry mouth, oral thrush, or geographic tongue.
- Hormonal Changes: Menopause and other hormonal fluctuations.
- Medications: Certain medications, including those for high blood pressure, can lead to BMS.
- Allergies: Reactions to foods, dental materials, or oral care products.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression have been linked to BMS.
- Medical Conditions: Diseases like diabetes, acid reflux, and thyroid problems.
Is Burning Mouth Syndrome Dangerous?
While BMS is not considered life-threatening, it can significantly impact the quality of life. The chronic pain and discomfort may lead to difficulties in eating, sleeping, and performing daily activities, potentially resulting in emotional distress. Therefore, seeking appropriate treatment is essential.
Burning Mouth Syndrome Treatments
Treatment for BMS focuses on alleviating symptoms and addressing any underlying causes. Options include:
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, doctors may prescribe medications such as:
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid: An antioxidant that may help reduce symptoms.
- Clonazepam: A medication that can help alleviate nerve pain.
- Capsaicin: Topical application may help desensitize nerve endings.
- Oral Rinses: Special mouthwashes designed to soothe the burning sensation.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): To address psychological factors contributing to BMS.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Burning Mouth Syndrome Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies may provide relief from BMS symptoms:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep the mouth moist and alleviate dry mouth sensations.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of tobacco, alcohol, spicy foods, and acidic beverages that can exacerbate symptoms.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, which can be irritating.
- Suck on Ice Chips: This can provide temporary relief by numbing the burning sensation.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to reduce stress levels.
- Dietary Adjustments: Ensure a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients to prevent deficiencies.
- Chew Sugar-Free Gum: This can stimulate saliva production, helping to alleviate dry mouth.
- Aloe Vera Rinse: Rinsing the mouth with aloe vera juice may soothe oral tissues.
- Baking Soda Rinse: A solution of baking soda and water can help neutralize acids and soothe the mouth.
While these remedies may provide relief, they should complement, not replace, professional medical advice.
What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Burning Mouth Syndrome?
Deficiencies in certain vitamins, particularly B vitamins like B12, folate, and B2 (riboflavin), have been linked to BMS. Ensuring adequate intake of these vitamins through diet or supplements may help alleviate symptoms.
Medications That Cause Burning Mouth Syndrome
Some medications have been associated with the onset of BMS, including:
- ACE Inhibitors: Used for high blood pressure.
- Antidepressants: Certain medications that impact nerve function.
- Diuretics: May cause dry mouth, exacerbating BMS symptoms.
How Long Does Burning Mouth Syndrome Last?
The duration of BMS varies. Some individuals experience symptoms for months, while others may have persistent discomfort for years. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can improve prognosis.
How to Stop Burning Mouth Syndrome?
To manage and reduce BMS symptoms:
- Identify and treat underlying conditions.
- Follow a nutrient-rich diet.
- Avoid triggers like spicy and acidic foods.
- Stay hydrated and practice good oral hygiene.
- Manage stress and anxiety.
Conclusion
Burning Mouth Syndrome is a challenging condition that can affect daily life, but relief is possible. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and reduce discomfort. If you experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Difference Between Impetigo vs Cold Sores
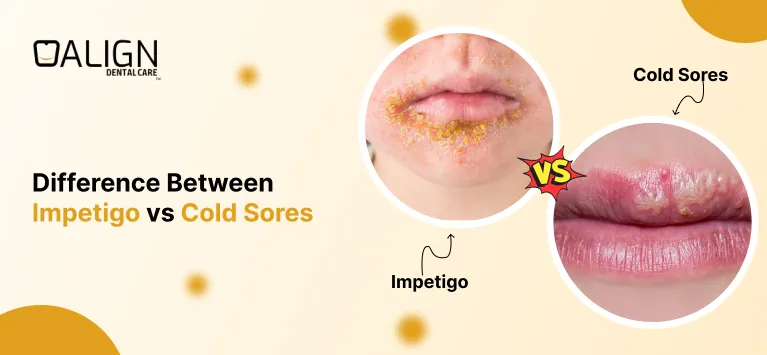
Impetigo and cold sores are both common and contagious skin conditions that often cause blisters around the mouth, but they differ in causes, symptoms, and treatment. In this blog, we will explore the key differences between impetigo and cold sores, including their causes, symptoms, appearance, and treatments. Understanding these conditions will help you identify them accurately and take the right steps to manage or prevent them.
Impetigo vs. Cold Sores: Key Differences
Here’s a detailed comparison of impetigo vs cold sores to help you understand their differences.
| Feature | Impetigo | Cold Sores |
| Cause | Bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus). | Virus (Herpes Simplex Virus, mostly HSV-1). |
| Appearance | Red sores that burst and form honey-colored crusts. | Fluid-filled blisters that scab over. |
| Location | Often around the nose, mouth, hands, and legs. | Usually on the lips or around the mouth. |
| Symptoms | Itchy, mild discomfort; possible swelling. | Tingling or burning sensation; can be painful. |
| Contagion | Through direct contact or shared items. | Spread via saliva, blisters, or direct contact. |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (topical or oral). | Antiviral creams or medications. |
| Duration | Clears in 7–10 days with treatment. | Resolves in 7–14 days; may recur. |
| Reoccurrence | Rare after treatment. | Common due to dormant virus reactivation. |
| Risk Groups | Mostly children; those with skin injuries. | Anyone exposed; triggered by stress or illness. |
| Prevention | Maintain good hygiene, treat wounds quickly. | Avoid direct contact; use sunscreen on lips. |
What Is Impetigo?
Impetigo is a common bacterial skin infection, especially in children. It typically occurs when bacteria enter the skin through cuts, insect bites, or scratches. It is caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Symptoms of Impetigo
- Red sores or blisters, usually around the nose, mouth, hands, or legs.
- The sores burst, leaving a yellowish or honey-coloured crust.
- Itching and mild discomfort.
- In some cases, swollen lymph nodes near the infection site.
How Does Impetigo Spread?
Impetigo is highly contagious. It spreads through:
- Direct contact with an infected person.
- Sharing towels, clothing, or other personal items.
- Touching surfaces contaminated with the bacteria.
Who Is at Risk?
While anyone can get impetigo, it’s most common in:
- Children aged 2–6 years.
- People with weakened immune systems.
- Those living in close quarters or hot, humid environments.
What Are Cold Sores?
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), usually HSV-1. They are a viral infections, not bacterial, and often recur throughout a person’s life.
Symptoms of Cold Sores
- Small, fluid-filled blisters, often on the lips or around the mouth.
- A tingling or burning sensation before the blisters appear.
- Blisters that burst and form a scab as they heal.
- Pain or discomfort around the affected area.
How Do Cold Sores Spread?
Cold sores are also highly contagious and spread through:
- Kissing or direct contact with an infected person.
- Sharing utensils, lip balms, or drinks.
- Touching the sores and then touching your face or others.
Who Is at Risk?
Anyone exposed to HSV-1 can get cold sores. They are often triggered by:
- Stress.
- Illness or fever.
- Sun exposure.
- Hormonal changes, like during menstruation.
Key Differences Between Impetigo and Cold Sores
Causes:
What Causes Impetigo?
Impetigo is caused by bacteria, primarily Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria enter through broken skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or insect bites. Poor hygiene or crowded environments often make it easier for this condition to spread.
What Causes Cold Sores?
Cold sores, on the other hand, are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). This virus can stay dormant in the body and reactivate during times of stress, illness, or a weakened immune system. Unlike impetigo, the cause is viral rather than bacterial.
This distinction is crucial because antibiotics treat bacterial infections like impetigo, while antivirals are used for viral infections like cold sores.
Appearance:
What Does Impetigo Look Like?
Impetigo often appears as small red sores that eventually burst, leaving behind a yellowish or honey-coloured crust. During the healing process, the affected area may look moist or wet. These sores are usually grouped around the nose, mouth, or other exposed skin areas.

What Does Cold Sores Look Like?
Cold sores start with a tingling or burning sensation. Soon after, small, fluid-filled blisters form. These blisters burst open and leave a painful ulcer before scabbing over as they heal. Cold sores are typically concentrated on or around the lips.
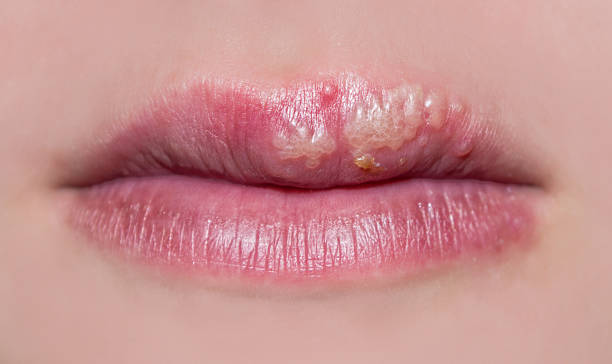
Where do Impetigo and Cold Sore Occur?
Impetigo commonly affects areas like the face (around the nose and mouth), hands, and legs. These are regions that are often exposed and prone to minor injuries, making them susceptible to bacterial infections.
Cold sores mostly appear on the lips or the area surrounding the mouth. In some cases, they can spread to the nose or even the inside of the mouth if the infection is severe.
Contagious:
Both conditions are contagious, but the mode of transmission differs.
Is Impetigo Contagious?
Impetigo spreads through direct contact with infected sores or items like towels and clothing. Sharing personal items increases the risk of transmission.
Is Cold Sore Contagious?
Cold sores are spread through saliva and close personal contact, such as kissing or sharing utensils, lip balms, or towels. Even when there are no visible sores, the herpes virus can still spread, making it more challenging to control.
Impetigo Vs Cold Sore Symptoms:
In impetigo, symptoms are usually mild and painless, but the sores may itch. Scratching can lead to further spread of the bacteria to other areas of the body.
Cold sores, however, can be painful and are often preceded by a tingling, itching, or burning sensation. As the blisters form, they may cause discomfort, making it harder to eat or talk comfortably.
How To Treat Impetigo And Cold Sores?
Treatment for both conditions varies based on their cause:
- Impetigo requires antibiotics, either as a topical cream or oral medication, to kill the bacteria and prevent complications. Proper wound care is also essential to manage symptoms.
- Cold sores are treated with antiviral creams or oral medications. Over-the-counter creams can help relieve discomfort, but prescription antivirals like acyclovir work better to reduce healing time.
Duration:
How Long Does Impetigo Last?
With proper treatment, impetigo usually clears up within 7–10 days. It does not typically recur unless re-infected.
How Long Do Cold Sores Last?
Cold sores last around 7–14 days and often recur due to triggers like stress, illness, or exposure to sunlight. This recurring nature is because the herpes virus stays in the body indefinitely.
Reoccurrence of Impetigo and Cold Sores:
Impetigo rarely reappears once treated. Maintaining hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals can help prevent it.
Cold sores, however, are known for recurring. Triggers like fatigue, stress, and weakened immunity can reactivate the dormant virus, leading to repeated outbreaks over time.
Can children develop both impetigo and cold sores?
Yes, children can develop both impetigo and cold sores under certain conditions.
- Impetigo in children: This is very common, especially in younger kids, as their skin is more delicate and prone to minor cuts or abrasions that allow bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes to enter. Impetigo often spreads in daycare or school settings due to close contact and shared items.
- Cold sores in children: Cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1), which can be transmitted through close contact, such as kissing or sharing utensils with someone who has the virus. While less common in very young children, they can occur if the virus is contracted early in life.
How to Prevent Impetigo and Cold Sores?
Preventing Impetigo
- Keep skin clean and dry.
- Treat cuts, scrapes, or insect bites promptly.
- Avoid sharing towels, clothing, or personal items.
- Wash hands regularly.
Preventing Cold Sores
- Avoid direct contact with someone who has an active cold sore.
- Do not share utensils, lip balms, or drinks.
- Use sunscreen on your lips to prevent sun-triggered outbreaks.
- Manage stress and maintain a healthy immune system.
When to See a Doctor:
- Impetigo: If the sores do not improve after a few days of treatment or if new sores keep appearing.
- Cold Sores: If outbreaks are frequent, very severe, or do not heal within two weeks.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and help you recover faster.
Final Thoughts
To summarize:
- Causes: Impetigo is bacterial, while cold sores are viral.
- Appearance: Impetigo forms red sores with honey-coloured crusts, while cold sores are fluid-filled blisters.
- Location: Impetigo affects exposed skin; cold sores are usually on or around the lips.
- Contagion: Both are highly contagious through contact or shared items.
- Treatment: Impetigo requires antibiotics; cold sores need antiviral medications.
Knowing these differences and prevention tips can help you better manage these conditions and seek timely medical care when needed.
Does Oil Pulling Whiten Teeth?

Oil pulling is an ancient practice that has gained modern-day popularity as a natural method to improve oral health. Swishing oil in your mouth is believed to help remove bacteria, plaque, and other impurities, leading to a cleaner mouth and fresher breath. While many people swear by its benefits, a common question remains: does oil pulling actually whiten teeth? In this article, we’ll explore what oil pulling is, how it works, the benefits it offers, and whether it can truly make your teeth whiter.
What is Oil Pulling?
A spoonful of oil, such as coconut oil, is swished in your mouth for 15 to 20 minutes while the oil is pulled. During this time, the oil binds to bacteria, plaque, and other impurities, which are then removed when you spit out the oil. It’s a simple process believed to promote oral health, freshen breath, and potentially reduce surface stains on teeth.
What’s the Origin of Oil Pulling?
Oil pulling is an ancient Ayurvedic practice dating back thousands of years. Originally from India, it was used as a traditional remedy to detoxify the body, improve oral health, and balance overall health. Traditionally, sesame oil was the most commonly used oil for this practice. Coconut oil gained popularity later due to its natural antibacterial properties, mild flavor, and easy availability, making it especially popular for oral care in the modern wellness community.
Benefits of Oil Pulling
Oil pulling has multiple potential benefits, including:
- Improved Oral Health: The swishing action helps remove bacteria and plaque, leading to a cleaner mouth.
- Fresher Breath: It can reduce the bacteria that cause bad breath, making your mouth feel fresher.
- Reduced Plaque and Gum Health: Oil pulling may reduce plaque formation by eliminating bacteria, helping support healthy gums.
Does Oil Pulling Whiten Teeth?
While there is no reliable scientific evidence that oil pulling whitens teeth, it can help make them look cleaner by removing surface stains and reducing bacteria. The practice mainly promotes better oral hygiene, which can lead to a brighter appearance over time. So, while it may not provide significant whitening, oil pulling can contribute to a fresher, healthier smile.
Choosing the Right Oil for Oil Pulling
When starting oil pulling, picking the right oil is essential. Look for oils with strong antibacterial qualities, a mild taste, and a smooth texture to make swishing more comfortable.
Here are some key factors to consider:
- Antibacterial Effect: The oil should help reduce harmful bacteria in your mouth.
- Nutrient Profile: Oils with high lauric acid content are great for fighting bacteria and viruses.
- Flavor and Texture: Choose an oil with a taste and texture you find pleasant, as it will be in your mouth for a while.
- Purity and Organic Quality: Organic, cold-pressed oils are best because they are free from chemicals and retain their natural benefits.
Best Oils for Oil Pulling
Several oils are popular for oil pulling, each offering distinct advantages:
- Coconut Oil: Known as one of the top choices, coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has strong antibacterial properties, helping to fight bacteria linked to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Sesame Oil: Traditionally used in Ayurveda, sesame oil is valued for reducing plaque and detoxifying the mouth. It’s a good choice for oil pulling due to its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
- Sunflower Oil: With its light flavor, sunflower oil is also widely used. It’s rich in Vitamin E, an antioxidant that supports healthy gums.
- Clove Oil: Clove oil is valued for its pain-relieving and antibacterial properties, making it helpful for soothing gums and reducing bacteria in the mouth.
- Neem Oil: Often used in Ayurvedic medicine, neem oil has potent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an excellent option for promoting oral health.
- Mustard Oil: Known for its warming effect, mustard oil helps improve blood flow in the gums, offering a unique benefit for maintaining oral health.
Each oil has unique properties, so you can choose one based on your preference.
How to Oil Pull
If you’d like to try oil pulling, follow these steps:
- Put About 1 Tbsp (15 ml) of Oil in Your Mouth: Coconut oil is a popular choice, but other oils like sesame or sunflower work too.
- Swish for 15-20 Minutes: Move the oil around your mouth gently. Avoid using too much force, as it may cause discomfort in your facial muscles.
- Spit Out the Oil: To avoid clogging your pipes, spit the oil onto a piece of paper and dispose of it in the trash.
- Brush Your Teeth: After oil pulling, rinse with water and brush your teeth as usual.
Tip: Some people prefer oil pulling on an empty stomach before brushing, often doing it in the morning while showering.
How Does Coconut Oil Whiten Teeth?
Coconut oil has natural antibacterial properties, which may help remove plaque and bacteria that can cause yellowing or dull teeth. When coconut oil binds with these impurities during swishing, it can help clear away surface stains, leaving teeth looking cleaner and potentially whiter. However, it does not chemically whiten teeth like traditional whitening agents do.
Financial Benefits of Oil Pulling
Oil pulling can be a cost-effective way to maintain oral hygiene. Compared to expensive whitening treatments and dental products, a jar of coconut oil is relatively affordable and can last several weeks to months. By potentially reducing plaque and improving oral health, it may also help cut down on future dental expenses.
Conclusion
While oil pulling may not directly whiten teeth like traditional whitening treatments, it can help reduce surface stains and improve oral hygiene, leading to a fresher and healthier-looking smile. Its ability to remove plaque and bacteria contributes to better oral health and can enhance the natural brightness of your teeth over time. With the right oil and regular practice, oil pulling can be a simple, cost-effective addition to your oral care routine.
Highlighting the crucial role of mouth moisturizers in oral well-being

Ever experience having a parched mouth? And to alleviate the dryness, do you require any kind of oral oasis? If you feel this way, you may have xerostomia, often known as dry mouth. Dry mouth, a frequent oral health disorder linked to less saliva, can cause problems with how your mouth works and major oral health problems.
The effects of a mouth moisturizer can mimic a momentary oasis for dry mouth. We’ll give you the lowdown on mouth moisturizers so you can make the best decisions for your circumstances.
What results in oral dehydration?
More than one individual has the sensation of having a dry mouth. Simply put, the mouth is dehydrated. This triggers a slight increase in saliva production, accompanied by discomfort in the oral cavity. Therefore, it’s crucial to rehydrate promptly. You’ll restore a positive attitude and proper oral equilibrium in this approach.
A dry mouth is an indication of dehydration. This is brought on by a number of unique causes. Water dehydration is the major cause of xerostomia. In other words, consuming this beverage in even a small amount prevents the tongue from retaining moisture. Additionally, the mouth cavity becomes dry after taking some drugs. These include analgesics or hypnotics, which have the side effect of drying out the mouth.
This soreness may also be brought on by a chronic illness, a periodontal condition, or an immunological disorder. Finally, xerostomia is caused by an issue with the salivary gland. The majority of the time, this final one emerges at night. You’ll likely have a strong urge to drink a lot of water, as well as a tendency for your mouth to feel quite pasty. This will be followed by a challenge with readily chewing food and the emergence of some fissures.
These will be evident at the level of the lips and hurt. Dehydration in the mouth can be detected by bad breath. You can see the dentist to find the cause of the issue as soon as these symptoms start to occur.
Guidelines for maintaining oral moisture
In order to properly keep your mouth moisturized, there are a number of techniques.
Maintaining oral hydration
Your mouth can be hydrated in the first step by being humidified. Indeed, water will give the mucous membranes of this cavity the essential hydration. This fluid is capable of performing the same function as saliva. The key argument in favor of drinking water frequently is this. Make sure the temperature is not excessively high or low.
You can, however, choose between employing a water or synthetic saliva sprayer. The nerves that power the salivary glands are stimulated by this accessory. If you have a history of respiratory issues, a physician must recommend the use of oral moisturizer due to the hazards involved.
Saliva activation with certain workouts
It is possible to produce saliva by following some fairly basic procedures. You may do this by chewing sweets or gum. If at all feasible, make them without sugar and mint-flavored. With the aid of a fresh breath, the salivation process may then proceed in the best manner possible. Additionally, several fruits and vegetables have the capacity to encourage salivation on a regular basis.
Reducing the use of tobacco
Smoking damages heart and lungs. Using of tobacco not only affects will eventually impact your oral health. The chemicals employed in its synthesis, change how saliva is produced in the mouth. Tooth decay and other oral problems are consequences of this dry mouth.
Proper dental care
Oral hygiene is one of the key habits to having a moisturized mouth. This will prevent xerostomia-related disorders from developing. These include periodontitis, gingivitis, plaque, and tartar. For this, brushing your teeth after each meal is necessary. Use toothpaste that doesn’t have a lot of fluoride when doing it.
This item could harm your salivary glands and gums. As recommended by the dentist, you might use mouthwash or dental floss to optimize your brushing technique. It’s crucial to refrain from using an alcoholic rinse solution.
The Foundation and Benefits of Mouth Moisturizers
Mouth moisturizers work as a replacement for saliva to treat dryness. A mouth moisturizer provides advantages even if it isn’t a perfect substitute for the healthy saliva your body generates. An oral moisturizer can temporarily alleviate that dry mouth feeling by putting a protective coating of moisture on your oral tissues.
Several medical sites suggest using a xylitol-containing over-the-counter mouth moisturizer. For this crucial component in any mouth moisturizer you purchase, check the label. You may also inquire about recommended or prescribed moisturizing products for dry mouth with your dentist.
Simply moisturizing your mouth for a few seconds helps alleviate the symptoms of dry mouth. Because switching from “Ugh” to “Ah!” Some advantages of dry mouth moisturizer include:
- They’re portable, so you can moisturize your mouth while you’re on the go.
- You can use mouth moisturizers as often as needed, depending on the specific product – some are available via prescription. (For some products, your dentist or doctor might provide instructions on how often to use a mouth moisturizer daily.)
- Hydrating your mouth can alleviate symptoms of dry mouth, like speaking challenges, eating discomfort, or swallowing difficulties.
- You can lessen your risk of developing infections, gum disease, and cavities. Mouth moisturizers aid in preventing the bacterial overgrowth that causes these oral health issues.
Long-Term Remedies for Dry Mouth
Moisturizers for dry mouth are a nice short-term solution, but they are not a dry mouth cure. The oral moisturizer’s benefits will eventually wear off, and sadly, your mouth will feel dry once more.
Visit your dentist and doctor so they can determine the underlying reason for your dry mouth and treat it for long-term comfort. Among the several underlying factors that contribute to dry mouth are:
- Anxiety and stress
- Dehydration
- Medication side effects
- Neurological and autoimmune problems
- Illnesses including diabetes, addictions, and sleep difficulties
Oral Care and Dry Mouth
In the event of experiencing dry mouth, it is highly recommended to counteract it by employing an oral moisturizer. Nevertheless, it is crucial to complement this action with consistent dental care practices and regular biannual dental check-ups. Given that dry mouth elevates the likelihood of developing cavities and other oral health complications, upholding a stringent oral hygiene regimen is of utmost importance.
A dry mouth moisturizer is an easy approach to temporarily control the symptoms of dry mouth. But for long-term relief and to rule out any underlying problems, make sure you see a doctor.
The importance of soft bristles for gum health

Gum disease is often caused by improper brushing techniques and hard brush bristles. People who prefer stiff-bristled toothbrushes often use force, even if they brush in small circular motions, as dentists recommend, rather than back and forth along the surface of the teeth.
For example, young people harm their gums by using a toothbrush with hard bristles. This is all the more dangerous because they are confident that they are brushing their teeth and gums correctly. They pay great attention to oral hygiene and, therefore, can cause damage to the sulci (gum lines) because they brush their teeth too often and too vigorously with a very hard-bristled brush.
Hard bristles increase excess pressure when brushing your teeth.
Brushing your teeth too vigorously, whether with a medium-hard or hard bristle brush, can potentially harm your gums without causing immediate discomfort. But as a result, the consequences will be disastrous: the groove deepens, the gum line slowly descends, and, over time, the neck of the teeth is exposed, and high sensitivity to pain appears.
Dentists in research, teaching, and practice recommend toothbrushes with soft and fine bristles. If the bristles of the brush are soft, then it will not cause any harm. If, in addition, the bristles are thin, then the grooves of the teeth are easily accessible, and such a brush carefully eliminates harmful bacteria. This is important since many bacteria accumulate in inaccessible places that can be easily damaged.
Soft bristle toothbrush: what are its advantages?
You should try to remember one fundamental thing: oral hygiene is essential to maintaining good oral health and avoiding problems related to poor hygiene. In the pursuit of resolving fundamental dental issues, the utilization of a toothbrush with soft bristles emerges as a captivating solution and a promising first step. It’s essential to note, as a starting point, that the primary issues involve tooth decay and gum difficulties, particularly gingivitis.
Here are the keys to making your oral cleaning an effective and efficient process, even if you have decided to buy and use a soft-bristle electric toothbrush.
Recommendations for toothbrush hardness
As it is widely acknowledged, the toothbrush stands as an essential instrument for maintaining oral health. Numerous options abound in the market, such as the gentle bristle dental implement. Toothbrushes from multiple brands and in various shapes and hardnesses are available.
Let’s first explore the hardness of toothbrushes because not all toothbrushes are the same, and not all take care of our teeth in the same way.
A prevailing misconception persists among many individuals, asserting that a toothbrush with firm bristles delivers markedly superior cleaning efficacy when compared to its softer-bristle counterpart. This belief, rooted in the idea that bristle hardness equates to enhanced cleaning, is fundamentally flawed.
In truth, using a toothbrush with harder bristles can be detrimental to both your enamel and gums, particularly if you observe noticeable bristle wear within a few weeks. Consequently, persisting with a toothbrush featuring excessive bristle hardness not only fails to improve cleaning but also poses a significant risk to your dental health.
On the contrary, soft or medium-hard toothbrushes are ideal. Indeed, in some special cases, several people try to purchase and use an ultra-soft bristle toothbrush, essential for those with more fragile dental conditions.
In general, however, if you brush correctly for at least two minutes and also use other supplements for correct oral hygiene, you will achieve effective dental cleaning without damaging your teeth. Remember that applying more pressure does not lead to better cleaning.
When it comes to toothbrush use, soft or hard bristles can make a difference. Let’s now see in the next paragraph how to perform correct oral hygiene.
Oral hygiene beyond brushing
The toothbrush, though unquestionably vital, should not be viewed in isolation. In tandem with a soft-bristle toothbrush, it is advisable to introduce complementary components like dental floss and mouthwash into your oral care regimen. So, an ideal brushing would include these steps:
- Morning: when you use your toothbrush, soft or hard bristles create different consequences. When brushing your teeth, it is recommended never using toothbrushes with hard bristles;
- Afternoon: brush your teeth immediately after lunch so as to eliminate most of the impurities and food debris present between the teeth;
- Night: deep brushing, use of dental floss or brushes to remove dirt accumulated during the day, and finally, use of mouthwash.
Don’t forget these steps to have good oral hygiene. Remember that at your clinic, they will certainly be at your complete disposal to answer any questions about your oral hygiene habits. Do not hesitate to contact your dentist without obligation. If you have decided to buy an electric toothbrush, soft bristles will be excellent, but know that traditional toothbrushes must be of medium or soft hardness because if they are very hard, they can wear away the tooth enamel. It is not necessary to use very hard brushes or to wring out the toothbrush too much to achieve good hygiene.
Occasionally, in pursuit of thorough dental cleaning, individuals may exert excessive force on their teeth and gums, potentially causing discomfort to their gums. This is precisely why we advocate for the utilization of a gentle-bristle toothbrush.
Remember
If you have to change your toothbrush, hard bristles should be avoided. In general, hard bristles are not recommended as their prolonged use over time can cause alterations to the gums, so the choice will generally be that of medium hardness.
However, in case of doubt, it is always advisable to consult a specialist dentist. Your dentist possesses intimate knowledge of your unique clinical circumstances, your dental structure, and your gum health. Consequently, they are well-equipped to prescribe the most effective toothbrush for optimal outcomes. Prioritize the well-being of your dental aesthetics and overall oral health.
Understanding the Impact of Bruxism on Teeth, Jaws, and Oral Structures

Bruxism is generally defined as strong clenching (clenching) and small movements (grinding) between the upper and lower teeth. During these movements, the extremely powerful forces of the masticatory muscles can be exerted separately from the chewing function itself.
Thus, such exposure can create problems with teeth, such as the appearance of pits in the enamel near the gums, increased tooth sensitivity, tooth mobility, pain when biting, and problems with the jaw joint. Researchers who have been studying bruxism for a long time have been discussing the topic of mental stress and emotional disorders. It is also discussed that aggression may be the reason why there is a significant weakening of certain brain structures in the production of norepinephrine and the formation of stomach ulcers in experimental animals.
The concept of stress management is based on the psychological background of which bruxism is a manifestation and the benefits related to the activity of the masticatory muscles in relieving stress-related symptoms such as stomach ulcers. Clenching and moving (clenching teeth) during bruxism is an emergency response during periods of mental distress in people to cope with stress.
Forms of bruxism
There are two forms of bruxism:
- Daytime (bruxomania) – teeth grinding, jaw misalignment, thumb sucking, and lip biting.
- Night – a more severe form that has a strong negative effect on enamel, stimulates tooth wear, and increases the load and general tension of the jaw. This disease can and must be fought. There is a special Botox that is injected into the jaw and normalizes its functioning.
Causes of bruxism
Bruxism is a complex condition with a variety of potential causes:
- prolonged stress and nervous tension
- malocclusion
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system
- inflammation of the facial nerve
- incorrect orthodontic treatment on braces
- side effects of psychotropic drugs and antidepressants
- Neurological or endocrine disorders: Parkinson’s disease, Raynaud’s syndrome, hyperthyroidism
- hereditary predisposition
- Teething in children
- A man with bruxism
Bruxism symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of bruxism can be the first step toward effective management. Symptoms may include :
- creaking, chattering, or grinding of teeth at night
- pain in the jaws, face, and neck, and headaches
- increased sensitivity of teeth
- weakening and erasing of teeth
- damage to tooth enamel, the appearance of cracks and caries
- pain when opening the mouth
- pain in the tongue, palate, or mucous membrane of the cheeks
- Insomnia, anxiety, depression, and fatigue due to poor sleep and prolonged pain
The Impact Of Bruxism On Teeth, Jaws, And Oral Health
Long-term effects of bruxism
Untreated bruxism can have major long-term consequences, including considerable damage to the oral cavity. Constant grinding erodes dental enamel, resulting in increased tooth sensitivity, irreversible tooth damage, and even tooth loss. Excessive pressure on the jaw muscles and joints can develop temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder, which causes discomfort and dysfunction in the jaw joint and the muscles that regulate jaw movement. Untreated bruxism can cause changes in face structure and appearance over time owing to persistent muscular stress in extreme instances.
Bruxism and dental damage
Bruxism is one of the primary causes of dental injury. Grinding can cause tooth loss, fractures, and even loosening of teeth due to the high pressure and friction. Excessive stresses can potentially harm or displace dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, implants, and fillings. It is vital to remember that this sort of damage jeopardizes not only the look of the teeth but also their functionality, perhaps making chewing and speaking more difficult. Furthermore, repair is sometimes complex and costly, stressing the need for early detection and management of bruxism.
Bruxism and systemic health
Bruxism can lead to a variety of greater health concerns in addition to oral health. Notably, it is a risk factor for temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems, which can cause substantial discomfort and impaired jaw function. Another typical side effect of bruxism is sleep disturbance, which can cause exhaustion, cognitive issues, and an increased risk of various health diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Furthermore, the prolonged tension and pain associated with bruxism can have a severe impact on mental health, resulting in greater stress and a lower overall quality of life.
Diagnosis of bruxism
There are several methods for diagnosing bruxism:
- Clinical examination: On examination, the doctor may see worn, broken, or cracked teeth, enlarged masticatory muscles, and other changes in the dentoalveolar system.
- Electromyography: This allows you to measure the activity of the masticatory muscles. This method helps to understand if you have bruxism and determine its severity.
- Radiography: Used to identify structural changes in the dental system due to bruxism.
- CT scan: Used to obtain more detailed information about the structure of the dental system and identify its changes.
Treatment of bruxism in Dentistry
Treatment of bruxism depends on its cause and includes different approaches:
- Bite correction: If bruxism is caused by a malocclusion, the doctor will perform orthodontic treatment using braces or other orthodontic devices.
- Use of removable night splints: For bruxism due to stress or sleep disturbance, removable splints are helpful to protect the teeth and relieve muscle tension.
- Use of medications: Muscle relaxants, antidepressants, and anxiety medications can help relieve muscle tension and reduce bruxism.
- Physiotherapy: Helps strengthen facial muscles, reduce pain, and relieve tension.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, such as violation of the function of the TMJ, surgery may be required.
Prevention of bruxism
To prevent bruxism, it is recommended:
- avoid stress;
- Do not drink alcohol or drugs because they worsen the condition of the nervous system;
- Consult a doctor if you have problems with the dental system, neurological or endocrine diseases;
- Treat your teeth in a timely manner and correct your bite.
If you notice symptoms of bruxism, consult a doctor immediately. Timely treatment will help to avoid complications and maintain healthy teeth.
To summarize
Bruxism is a complicated sleep problem that can have serious effects on dental health and general well-being. It is critical to recognize its indications and symptoms, such as teeth grinding, jaw discomfort, and dental damage, in order to intervene early. If left untreated, bruxism can cause long-term dental problems such as tooth sensitivity and TMJ difficulties, as well as systemic health issues and a lower quality of life. Depending on the reason, many diagnostic procedures and therapy options are available. Stress management and getting expert treatment when symptoms occur are part of the prevention process. Remember that prompt action is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and a pain-free lifestyle.
Causes, Impacts, and Strategies for Managing Xerostomia

Saliva, or spit within your mouth, plays an important role. It aids in the chewing and swallowing of food and protects your mouth from bacteria and tooth decay. When your spit glands do not produce enough saliva, a condition known as xerostomia occurs. This might cause your mouth to feel dry and unpleasant.
What is Xerostomia?
Xerostomia or dry mouth syndrome is an alteration of the salivary glands that produces an unpleasant sensation of dry mouth. The saliva decreases, and it acquires a viscous and foamy texture. The sense of taste is altered, and a sensation of pain and burning appears on the tongue.
Beyond the annoying sensation, it can trigger more serious problems. It usually causes dryness, irritation, and cracking in the mouth’s soft tissues, which puts the patient at risk of attack by microorganisms. Because saliva also serves as an antiseptic in the oral cavity, when its production declines, the risk doubles, and the mucous membranes and gums may become inflamed (gingivitis), or cavities, painful ulcerations, and halitosis may emerge.
Dry mouth syndrome can cause digestive and respiratory problems, including pharyngitis, dyspepsia, and constipation.
Causes of dry mouth syndrome
Dry mouth can be caused by several circumstances, including the following:
Medications
Certain pharmaceuticals, such as antihistamines, decongestants, and blood pressure medications, can cause dry mouth.
Aging
While dry mouth is not a natural result, older people tend to take more drugs, some of which might cause it.
Cancer treatment
Radiation therapy to the head and neck can cause salivary gland damage, resulting in decreased saliva production. Chemotherapy can also cause changes in the content and amount of saliva.
Injury or surgery
A dry mouth can be caused by an injury or surgery to the nerves in the head and neck area.
Tobacco use
Both chewing and smoking tobacco might increase the likelihood of developing dry mouth.
Dehydration
A lack of fluid intake might result in dry mouth.
Hot weather and physical activity
The salivary glands can dry when the body’s fluids are diverted elsewhere during exercise or exposure to heat.
Certain health conditions and habits can contribute to dry mouth, including anxiety and depression, HIV and AIDS, poorly managed diabetes, Sjögren’s syndrome, sleeping with an open mouth, snoring, and stroke or Alzheimer’s disease (though these may cause a sensation of dryness even if the salivary glands are functioning normally).
Risk factors
- Although aging is not a direct cause of dry mouth, older individuals are more prone to having dry mouth because They frequently use drugs that might cause dry mouth.
- They are likelier to have health conditions that cause dry mouth (such as type 2 diabetes).
- They have a lowered thirst perception and may be dehydrated.
- Tobacco usage can also exacerbate symptoms, regardless of age.
Symptoms of Dry Mouth
In addition to the perception of dry mouth, people suffering from this problem may also have problems with:
- Burning sensation in the mouth.
- Thick and dense saliva.
- Altered sense of taste (dysgeusia) and perception of a bitter mouth.
- Tongue reddened and smooth, with loss of filiform papillae.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Split and chapped lips.
- Halitosis.
- Mouth ulcers.
- Cavities.
- Periodontitis.
- Candida albicans infections of the mouth.
People who suffer from dry mouth, particularly those suffering from Sjögren’s syndrome, are more susceptible to developing gastroesophageal reflux disease. More prone to gastroesophageal reflux, which appears as retrosternal burning.
Site inflammation of the main salivary glands is also characteristic in these patients, manifested by swelling associated with local pain.
Xerostomia: clinical manifestations
Because a reduction in saliva production largely defines xerostomia, clinical symptoms of this condition include different harmful effects of dry mouth on the body.
In the lack of enough saliva in the oral cavity, for example, suppuration occurs, the risk of acquiring fungal infections rises, and the impression of food flavour changes.
This illness progresses through multiple stages:
- Xerostomia is difficult to detect in the early stages since the submandibular and parotid salivary glands continue to release adequate saliva, and pain is felt only after a long talk.
- In the future, saliva production decreases, resulting in the so-called partial decompensation stage during which eating becomes so tough that going without water becomes impossible.
- The salivary glands nearly totally stop operating during the third phase. This causes a variety of mouth disorders, such as stomatitis, glossitis, and oral mucosa diseases. These problems include erosion, ulcers, chapped lips, and sores in the corners of the mouth.
- Seizures, recurrent sore throats, painful throat complaints, and the development of chronic periodontitis are also noted in addition to the major signs. Patients with removable dentures experience difficulty with their procedure because their tongue turns bright red.
Treatments and Strategies for Managing Xerostomia
The first and most important step in dealing with xerostomia is diagnosing the problem. The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient to learn about their medicines and previous dental operations. Tests such as sialography and salivary gland ultrasounds are used to diagnose xerostomia.
Symptomatic treatment of xerostomia provides patients with short relief. However, determining the etiology of the disease is critical. When xerostomia is caused by medicine, it is generally simple to give aid. However, the odds of recovery are significantly reduced for people who have received radiation therapy due to probable interference with salivary gland function.
During treatment, a special role is played by pathogenetic therapy aimed at combating the causes of xerostomia. For treatment, novocaine is applied to the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. As well as the following procedures: electrophoresis, galvanotherapy, and vibration massage.
To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to increase the consumption of pure still water. Lollipops (preferably natural and with a sugar substitute) and chewing gum are also suitable.
Avoid dry and salty foods and alcohol – including alcohol-containing mouthwashes. Quitting smoking and choosing a toothbrush with softer bristles is recommended.
The healing process depends on a number of factors, but in most cases (excluding cases of atrophy of the salivary glands), if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the prognosis is favourable.
Conclusion
Xerostomia, characterized by dry mouth due to reduced salivation, poses various challenges and impacts on oral health. While it can result from multiple causes, including medication side effects and underlying conditions, prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential. Managing xerostomia involves symptomatic relief, addressing its root causes, and adopting oral hygiene measures. Adequate water intake, avoidance of certain foods and habits, and medical interventions can alleviate discomfort. With proper care, the prognosis for xerostomia can be favourable, improving overall oral well-being.
10 tips to get rid of dental anxiety

Do you find visiting the dentist terrifying? Despite being more prevalent, dental anxiety is easily manageable.
Your oral health will be negatively impacted if you cannot overcome your dental phobia. So throw your fear out by knowing what dental anxiety is and including its symptoms, reasons for existing, and some tactics and strategies for overcoming it in this blog post.
Read on to overcome your phobia!
Dental anxiety: What is it?
Dental anxiety is the anxiety, dread, or tension related to a dental environment.
Odontophobia, often known as dental phobia, is a relatively frequent cause of people skipping their scheduled exams for oral health. Some individuals are genuinely terrified to visit the dentist.
Signs and symptoms of dental anxiety
Here are some symptoms that indicate you have dental anxiety.
- Increase in heartbeat rate
- Using humor or aggression to disguise nervousness
- Low blood pressure
- Sweating
Causes of dental anxiety
- Fear of pain
- Poor experience
- Embarrassment in allowing others to touch your mouth
- Fear of needles and drill sound
- A poor impression of dentists
- Panic due to claustrophobia
Tips and tricks to overcome dental anxiety
We know that there will always be remedies if there is an issue. Here are some tips and tricks for a calm and relaxed dental checkup.
Pick the ideal dentist for yourself.
First and foremost, you must select a reputable dentist who specializes in helping those who have anxiety and fear of the dentist. Additionally, pick a dentist who treats you well and who gets positive feedback from their present patients.
Share your anxiety.
Sharing your feelings can have a significant impact on how things turn out. Discussing your fears with your dentist may help you overcome them and maintain your comfort. There are others you can discuss your anxiety with besides your dentist. You can seek counseling or talk to your friends and family about your anxiety.
Deviation may be advantageous.
If there is a television in the clinic, you can watch films, videos, and other media there. If not, you can use your tablet or mobile device. Get relaxed by endeavoring deviation strategies like hearing your favorite playlists, audio files, and podcasts. Even engaging in conversions helps you distract from dental fear.
Engage in deep breathing exercises.
Breathing is the key to remaining calm and relaxing in some situations. Breathing can bring physiological changes to our body, like reducing the heart’s pulse rate and lowering blood pressure. Additionally, the blood stress level can also be lowered.
CBT (Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy).
CBT is a form of psychological treatment. It will help people manage mental health conditions like stress, depression, phobias, and anxiety. This treatment approach helps you recognize negative thoughts and find ways to replace them with positive ones. So, this therapy can be used to treat dental phobia and its associated conditions.
Request for sedative solutions.
Sedatives are one of the options. Ask your dentist about sedatives using relaxation techniques if you cannot reduce your anxiety. During dental procedures, sedation is used to keep you comfortable. Nitrous oxide, oral conscious sedation, and intravenous (IV) sedation are available.
Bring a support person along.
A friend can sometimes be all you need to grasp your hand and reassure you that everything will be good. Ask a friend or member of your family to accompany you if you’re nervous about receiving therapy. A friend may sit by your side in the room during the procedure.
Skip the caffeine.
Before a dentist appointment, pay attention to your food. It’s common knowledge that foods heavy in sugar and caffeine can cause jitters, so it’s best to avoid them before your visit. Instead, opt for protein-rich foods, as they have a soothing influence.
Establish non-frantic times for your appointments.
Choose a time for your appointment that is convenient for you. Avoid rushing to your appointment on time because doing so will make you uptight and anxious. You might find it beneficial to lessen your worry when fewer patients are scheduled.
Take breaks.
You can relax for a while between dental procedures by taking pauses. You can utilize a few signs to let your dentists know you need a rest. As a result of your mind and body relaxing when needed, this will lower your anxiety level.
Bottom Line
It’s not difficult to overcome your dentophobia. Your dental anxiety should never take you away from your path toward maintaining excellent oral hygiene. It’s essential to be open about your anxiety, consult a dentist, and share your problems. Follow these tips to eliminate anxiety and maintain excellent oral hygiene through regular dental checkups.